Züs Security
Own and control your data with unmatched security and privacy
Prevent Hacks and Breaches at Server with Data Fragmentation and Split-Keys. Prevent Ransomware at Client with Split-Keys.
Prevent Hacks and Breaches at Server with Data Fragmentation and Split-Keys. Prevent Ransomware at Client with Split-Keys.
Recently discovered pitfalls of Encryption Encryption ≠ Security 1, 2

Attackers can inject malicious keys into the encryption process

Attackers can force protocol downgrades, preventing encryption

Allows malicious servers to intercept & replace encryption keys

Files are renamed or relocated maliciously, leading to data loss

Attackers can modify or replace data chunks without detection

Attackers insert malicious files & folders leading to data breach

Attackers modify encrypted files undetected, corrupting data

Embedding passwords in shared links are intercepted
The master key is anchored on the blockchain, ensuring a unique and verifiable ID.
Enterprise securely stores master key in zVault, generating Split Keys for operational use.
Split Key is in all Clients and Servers making the master private key impenetrable to internal and external breach.
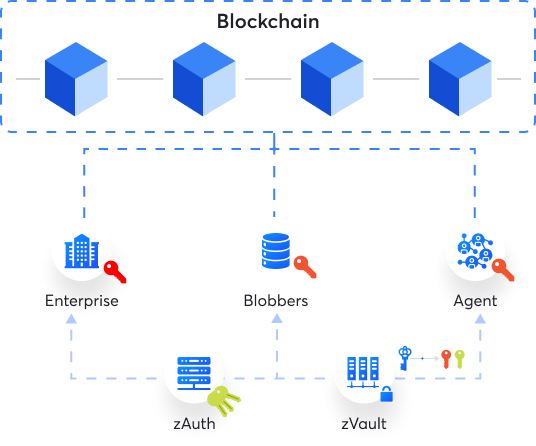
Data contract between Client and Servers is recorded on the blockchain.
An update to the CrowdStrike agent led to a widespread IT outage, impacting millions of Windows devices. Most of the backup images used BitLocker encryption, but the encryption key was stored in a Windows server affected by the outage and so it prevented recovery.
If Zus is used to store the backup, then the Windows user has full ownership and complete control of the key since it's part of a public blockchain network like a typical crypto wallet. Additionally, since the data is inherently fragmented over multiple data centers, the backup image need not be encrypted to restore devices.
In February 2024, Change Healthcare, a major operator of health payment processing in the US, was hit by a ransomware attack, where the hackers used malware to encrypt the company's systems, preventing access.
If the data is on Zus, it will be distributed over multiple data centers which will make it hard for the attacker to infect all the servers, since they would need to attack the IT operator of each server and try to phish them into installing the malware.
Other related terms: Spoofing, Hijacking, Eavesdropping, and Phishing. In 2017, Equifax data breach exposed over 143 million Americans. The issue was that the website used a shared SSL for hosting—with thousands of other websites using the same certificate. DNS (through fake websites) and SSL spoofing took place to redirect users to a phony website to intercept data from the site.
If Zus storage is used for hosting, the traffic is protected and the man in the middle does not have enough information to reconstruct the content, since data is stored in fragments across multiple datacenter servers.
The SolarWinds hack, also known as the SolarWinds supply chain attack, when the attackers inserted malicious code into SolarWinds' software platform, which was distributed to approximately 18,000 customers through routine updates. The malicious code, known as SUNBURST, created a backdoor in the infected systems.
This allowed the attackers to install additional malware and exfiltrate data without being detected for an extended period of time. The attackers used obfuscation, legitimate network tools and credentials to exfiltrate data through DNS requests, making it harder to detect the malicious activity among normal network traffic.
If all 3rd party software vendors use Zus to store their updates, then you’ve a higher guarantee that authenticated users on the Zus network have released the software,
The 2016 Democratic National Committee (DNC) Email Phishing Attack involved sending phishing emails to members of the DNC, including campaign chairman John Podesta, which looked like a Google security alert, urging him to change his password. When he clicked on it, he was directed to a fake Google login page, which allowed the attackers to gain access and leak data.
If an app reinvents and uses Zus for their storage, then their customer login process can use its serverless 2FA (two factor authentication).Most people don’t use traditional 2FA because it's a nuisance to go through during login. On Zus, it can be always on, and operate silently, seamlessly and without intrusion, and can be used for all file operations, something that doesn't exist today.
In mid-July 2024, Azure Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) experienced a significant outage caused by a configuration issue.
If an app reinvents and uses Zus storage and its serverless 2FA, then users are not dependent on an authentication server and will never experience an outage issue. The communication between the devices is done through BLE in close proximity to the user. Also unlike traditional 2FA which is used just for login, Zus 2FA is always on and is used for all file operations, something that doesn't exist today.
In March, several French state services were targeted by a cyberattack over a day with over 300 web domains and 177,000 IP addresses impacted, including severe disruptions to major public service websites.
If the websites put their JS code bundle and assets on Zus as a primary storage and use a shareable link to render their websites on any instance then even if the primary is DDoSed, any instance can be brought up instantly in an another datacenter and render the site seamlessly. The attacker would then need to attack this new datacenter and try to penetrate their defenses to DDoS the new server.